Disproportionate status
In China's non-ferrous metal products, the international market share of lead, tin and zinc has been high in the past, but it has been greatly reduced in recent years. The international market share of aluminum and copper has risen and then declined, but overall it is still at a low level. At present, only the international market share of nickel is on the rise.
The international market share of these six non-ferrous metals is generally not very high. After reaching a high of 8.2% in 2004, it quickly fell back. In 2007, the international market share was only 4.1%, only half of that in 2004.
The current low market share of the non-ferrous metals industry in the international market is not commensurate with China's status as the world's largest producer and consumer of non-ferrous metal products.
Low index
China's non-ferrous metals industry trade competitiveness index is low, except for 1990 and 1991, the other years are negative, and remain at a low level. The trade competitiveness index in 2000 and 2001 was below -0.4, and it remained at around -0.3 from 2002 to 2006. In 2007, the index fell to -0.4. This shows that the international competitiveness of China's non-ferrous metals industry is still very weak.
Generally speaking, China's non-ferrous metal industry is in the middle of the international market, but compared with the development trend of other countries' international competitiveness, the international competitiveness of China's non-ferrous metals industry is declining in recent years. This is a problem that needs to be of particular concern to the industry.
One liter and one sharp contrast
Russia, Canada, and Australia are major exporters of non-ferrous metal products. Russia and Canada generally have an international market share of more than 10%, and Australia's international market share has remained at around 8%. China's international market share of non-ferrous metal products also has a certain scale, ranking ahead of Brazil, Germany, the United States and other countries.
From a trend perspective, the international market share of the non-ferrous metals industry in most countries has remained stable, but China's international market share has shown a downward trend. This is in stark contrast to Japan’s rising international market share.
Who has an international competitive advantage
Australia, Russia, Canada, South Africa and Brazil have significant trade competitiveness advantages. The trade competitiveness index of the United States, Japan, Germany, France, South Korea, the United Kingdom, and China is basically negative and does not have the advantage of trade competitiveness. Compared with other countries, China is in the middle of the game.
In recent years, the UK non-ferrous metals industry trade competitiveness index has been rising, while China has shown a downward trend. In 2007, the UK non-ferrous metal industry trade competitiveness index surpassed China for the first time.
According to the comprehensive international market share and trade competitiveness index, the non-ferrous metals industries in Russia, Canada, Australia, Brazil and South Africa all have strong international competitiveness. The non-ferrous metals industry in other major countries including China is not currently Have an international competitive advantage.
Serious discomfort
Compared with Russia, Australia and other countries, China's non-ferrous metal industry competitiveness indicators are not performing well. This is related to the long-term exploration of mineral resources in the industry, resulting in shortage of resources, low industrial concentration, overcapacity, extensive economic growth, and energy saving. It is related to the arduous task of reducing emissions. In addition, the non-ferrous metal products have special financial derivatives properties, which makes the non-ferrous metal industry show serious incompatibility when the financial crisis strikes.
Performance 1: The price of domestic non-ferrous metal products has “diving†a lot. According to the researchers' monitoring data on the spot market of non-ferrous metals in large and medium-sized cities, by the end of 2008, the average price per ton of copper, aluminum and zinc was 29,574 yuan, 11,928 yuan and 10,125 yuan, respectively, down 51.42 compared with the same period in 2007. %, 35.34%, 50.39%.
Performance 2: The growth of domestic non-ferrous metal products is slow, and the growth rate of industrial added value is slowing down. According to statistics, from January to December 2008, the output growth of non-ferrous metal products fell sharply month by month, and even there was a negative growth. At the same time, the added value of enterprises above designated size in the non-ferrous metal mining and mining industry and non-ferrous metal smelting and rolling processing industries also fell sharply. Especially in November, the value-added growth of enterprises above designated size in non-ferrous metal smelting and rolling processing industries was only 0.5%. .
Performance 3: Inventories of domestic non-ferrous metal enterprises increased, and economic benefits fell sharply. The deepening of the international financial crisis has caused a significant reduction in the import and export trade of China's non-ferrous metals industry. The price of non-ferrous metals has also caused the domestic enterprises to purchase non-ferrous metal products to show a wait-and-see attitude. Manufacturing enterprises have delayed the purchase of digested inventories as much as possible, which has made the sales of domestic non-ferrous metal products unsatisfactory and the economic benefits have been seriously degraded.
The financial crisis has also had a major negative impact on the non-ferrous metal recycling industry, as follows:
First, enterprises have stopped production, employees are on holiday, and employees are unemployed. According to the statistics of the Recycling Metals Branch of the China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association, during the worst period of the financial crisis, more than 85% of the capacity of reclaimed refined copper was in production, and more than 70% of the copper produced by the scrap copper was discontinued, recycled aluminum and recycled lead. The production capacity is 50% and 60% respectively. More than 90% of enterprises have layoffs, and 300,000 people are facing unemployment.
Second, the company has a serious loss. When the financial crisis was severe, the decline in the price of non-ferrous metals directly led to a fall in scrap metal prices, and most of the scrap metal prices fell by more than 50%.
Increase industrial support
Under the influence of a package of economic stimulus plans, especially the "Non-ferrous Metals Industry Adjustment and Revitalization Plan," China's non-ferrous metals industry has emerged from difficulties. The next step is how to make the non-ferrous metal industry further adjust its industrial structure, change its development mode and enhance its international competitiveness while maintaining a rapid development momentum.
In terms of policy measures, China can consider increasing industrial support in the following aspects:
First, improve the collection and storage mechanism to achieve the rolling development of funds for collection and storage. In view of the high price of non-ferrous metal products and the completion of the non-ferrous metal industry's growth-maintaining tasks, China may consider suspending the collection and storage of non-ferrous metals. Non-ferrous metal storage institutions can even sell the non-ferrous metals from the stockpiles to stabilize the current over-the-counter non-ferrous metals market, and the profitable funds can be used for future storage and storage, achieving rolling development.
Second, dynamically adjust the export tax rebate policy. Before the outbreak of the financial crisis, in order to restrict the export of “two high and one capital†products, China basically canceled the export subsidy policy for non-ferrous metal products, and even imposed export tariffs on some non-ferrous metal import and export products. After the outbreak of the financial crisis, China has adjusted these policies in a timely manner. The purpose of the export tax policy adjustment is to maintain growth, and the current non-ferrous metal “guarantee growth†task is completed well, so we can consider adjusting the export tax rebate policy for non-ferrous metal products. In this way, it is possible to avoid the problems of anti-dumping and countervailing that occur frequently in the international arena, and to promote the transformation of the non-ferrous metal industry.
Third, actively promote the pilot of electrolytic aluminum direct purchase. According to the actual situation of high voltage level of electrolytic aluminum and low transmission cost, the direct reduction of electricity purchase cost of electrolytic aluminum is appropriately reduced, and the direct purchase power policy is implemented. In addition, China must increase investment control in non-ferrous metal smelting projects and accelerate the elimination of backward production capacity: on the one hand, it is necessary to set higher standards for energy conservation, environmental protection, land and technology, control new projects, and strictly implement national industrial policies. Newly built and expanded electrolytic aluminum and alumina projects. On the other hand, it is necessary to speed up the elimination of backward production capacity, eliminate the backward production capacity of lead and zinc smelting according to regulations, and establish a perfect exit mechanism for backward production capacity.
Fourth, formulate relevant preferential policies and vigorously support enterprises to implement the “going out†strategy. Today, China's non-ferrous metal mineral resources continue to rise in external dependence. To solve the shortage of non-ferrous metal mineral resources must have a global perspective, which determines that China's non-ferrous metal enterprises must vigorously implement the "going out" development strategy. After a long period of sustained and rapid development, domestic enterprises have formed a strong technical, capital, equipment and human resources advantages, and have a certain degree of competitiveness in the international arena. Enterprises must implement the “going out†strategy, and seek cooperation and competition with multinational mining companies to continuously enhance their international competitiveness in dynamic cooperation and competition. The relevant state departments should speed up the formulation of specific implementation policies for the “going out†strategy, including the simplified approval procedures for overseas resource development projects, financial, taxation and financial policy support, and at the same time establish and improve the foreign exchange management guarantee mechanism and coordination among relevant central departments. mechanism.
Optical Crystals Aspherical Lens
China Star Optics has strong and comprehensive technical capability, integrate the design and manufacture as a whole.Imported the global advanced aspherical equipment and instruments,manufactured various aspherical products,including infrared material Zinc Selenide (ZnSe),Germanium (Ge),Silicon (Si),Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) etc. Aspheric lens has already application in various high technology project and products.
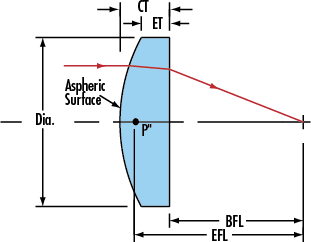
Aspheric Lens
Specification of our Aspherical Lens as follow:
Material:BK7,B270 glass,PYREX,ZF13 or other optical infrared material Zinc Selenide (ZnSe),Germanium (Ge),Silicon (Si),Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) etc.
Size:10mm-200mm
Fringes:lambda/2
Center Thickness:15nm-25nm
Dispersion round:0.03mm-0.2mm
Centration:3 arc min
Surface Quality:60-40 Scratch/Dig
Clear Aperture:90%
Coating:Available upon Request
Optical Crystals Aspherical Lens,Optical Aspheric Lens,Ir Glass Aspheric Lens,Infrared Glass Aspherics Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com