Recently, the team of Liu Jianjun, a researcher at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the team of Huang Yunhui, a professor at Huazhong University of Science and Technology, have designed a three-dimensional folding fan arrangement of organic conjugated molecules and transition metal ion coordination to build a nano-metal organic framework (MOF) material Zinc formate (Zn-PTCA) is the first breakthrough in the electrochemical activation of conjugated carbocyclic sodium storage, which greatly improves the sodium storage capacity of electrode materials and provides new ideas for the further design of new high specific capacity electrode materials. Related research results were published in Chem magazine. MOF nanomaterials with a three-dimensional pore structure are mainly self-assembled by transition metal ions (or nanoclusters) and organic ligands. Due to the characteristics of easy pore structure adjustment, high specific surface area and abundant surface functional groups, they are used in gas adsorption and separation. Nano-catalysis has been widely used. However, due to the limited specific capacity, the application of electrochemical energy storage materials is greatly limited. Taking sodium ion battery materials as an example, the sodium storage sites of metal organic electrode materials in sodium ion batteries are mainly concentrated on the surface rich functional groups (C = O, C≡N). Double bond rearrangement mechanism realizes electronic stable storage. However, sodium ions with a large radius are difficult to intercalate between the layers of the organic conjugated framework of the MOF material, and the intercalation of sodium ions to the van der Waals force between the layers and the weak force with the conjugated carbon ring cause the sodium ions It is difficult to store in organic structure skeleton conjugated carbon ring (sp2-C), which leads to lower reversible specific capacity of MOF materials. Therefore, the electrochemical activity of activated conjugated carbocyclic sodium storage is very important to improve the storage capacity of electrode materials, but it is more challenging. The team of Liu Jianjun combined first-principles computational electrochemistry, molecular dynamics simulation, and electronic structure analysis to find that the three-dimensional folding fan-shaped metal organic material has the characteristics of conjugated carbocyclic sp2-C to store sodium ions, and realizes conjugated carbocyclic storage Sodium's theoretical design and experimental verification. It was found that replacing sodium ions with a stable six-coordinate transition metal can transform layered sodium perylene tetraformate into three-dimensional fan-shaped zinc perylene tetracarboxylic acid, and the transition metal coordination chemical bond replaces van der Waals force between organic layers to form an open space. The structure not only eliminates the effect of sodium storage on van der Waals forces, but also increases the migration kinetic rate of Na +. The calculated electrochemical results are in agreement with the experimental electrochemical characterization, and all confirm that the two-step sodium intercalation reaction of Na + with the functional group -COO-, Na + and the conjugated carbocyclic sp2-C in Zn-PTCA reaches an equivalent of 357 mAh g-1 High specific capacity. The in-situ XRD, NMR, and infrared spectroscopy characterization of the charging and discharging process show that the structural framework still has good stability at low discharge voltage and after many cycles. The research work was supported by the National Key R & D Program, the National Natural Science Foundation General Project, and the Shanghai Materials Genome Project.
Optical Mirrors are designed to reflect light for a variety of applications, including beam steering, interferometry, imaging, or illumination. Optical Mirrors are used in a wide range of industries, such as life sciences, astronomy, metrology, semiconductor, or solar.
Metal coated mirrors are made of protected UV Enhanced Aluminium, Aluminium (Al), protected Gold (Au), protected Silver (Ag) coatings.
Broadband Dielectric Laser Mirrors are designed with high reflectivity across a wide range of wavelength.
it's ideal for UV, Visalbe,and NIR spectral ranges for beam steering applications
Protective Gold Mirror,Enhanced Aluminium Mirror,Protective Silver Mirror,Dielectric Coating Mirrors,Concave Mirror,Hot Mirror,Cold Mirror Changchun Ruiqi Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.ruiqi-optics.com
Structural design from Na-PTCA to Zn-PTCA and predicted sodium storage sites 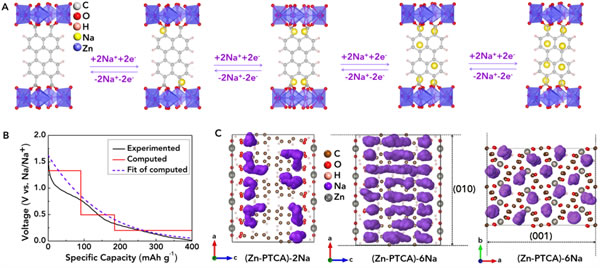
Intercalation site (A), intercalation voltage (B) and migration channel (C) of sodium ions in Zn-PTCA 
Electrochemical performance of Zn-PTCA: charge-discharge curve (A), cycle performance (B), rate performance (C) and CV curve (D)