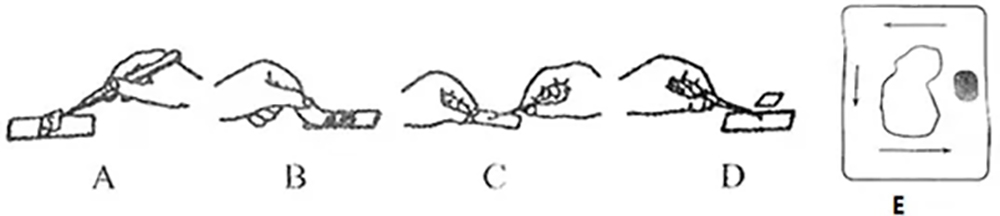
Conventional machining methods typically use larger tools to machine at lower speeds. In general, larger tools are not designed to perform more complex machining. In order to process with a micro tool, a conventional machine tool must be operated at a low speed, and the micro tool is brittle and easy to break. Larger tools have a higher resilience to the force of the chips due to their greater mass. Conversely, smaller tools are more susceptible to breakage due to greater brittleness. Poor chip removal is one of the main causes of tool damage. In fact, microtools that are damaged by poor chip removal are more than microtools that are damaged by unreasonable cutting parameters. To minimize the possibility of tool damage, the chips must be quickly removed from the cutting zone. Microtools require high spindle speeds during machining, and even higher spindle speeds for fast chip evacuation. Definition of tool size and machining speed: “Micro-tools†include milling cutters and drills with a diameter of 0.250′′ (6.35mm). These small-diameter tools are essential for complex and fine machining, and high-speed spindles are used for optimum machining. The effect of "high-speed cutting" is not yet defined and absolute parameters, but a usable reference definition is that the spindle speed is above 25000r/min and can be called high-speed cutting. "Three Elements" solution Three related factors to improve the efficiency of micro tooling include the optimal design of micro tools, the use of low viscosity coolants and high speed cutting technology. (1) Design of micro tools Miniature tools that simply scale down the geometry of larger diameter tools are often difficult to achieve efficient feed and achieve satisfactory machining accuracy. As the tool diameter decreases and the spindle speed increases, the tool requirements also change. Conventional tool designs with machine clamps are not suitable for the machining requirements of micro tools. This is mainly because the requirement for increasing the speed of the tool is not limited to the reduction of the tool diameter. The increased speed requires a better balance of the tool and a larger chip space to ensure smooth chip removal and prevent built-up edge. The use of micro-tools for efficient high-speed machining requires specialized optimization of the tool. The correct geometry of the micro-tools, combined with the high-speed spindle machine and reasonable cooling, completely eliminates the need for secondary machining to remove burrs. (2) Optimization of cooling method When using high-speed machining with micro-tools, a lot of cutting heat is generated, so some measures are needed to cool down. While high-speed cutting has certain advantages in reducing heat of cutting, high-speed cutting techniques alone are not sufficient to completely solve the cooling problem, so an effective cooling system is still required for some processes. The cooling system eliminates heat of cutting and also lubricates the tool for fast cutting on the workpiece surface. Trying to cut a piece of cold butter with a cooled knife is quite difficult because the knife is not lubricated when it is cut through the butter surface. But if the knife is heated, it melts a little butter, which lubricates the knife, making it easy to cut butter. Next page Microscope Slides And Cover Slips 1. The glass slide is used to put the sample to be tested, and the cover glass is covered on the sample to be tested.
6. The cover glass is square, the slide glass is rectangular, and the width is longer than the side of the cover glass.
microscope slide and cover slip,microscope slide and cover slip cube,microscope slide dimensions and cover slip Yong Yue Medical Technology(Kunshan) Co.,Ltd , https://www.yongyuetube.com
Today, the variety of workpieces is increasing, and the size of the workpiece is shrinking. The trend toward miniaturization requires that manufacturing processes must undergo changes. This growing demand requires people to rethink how to achieve more efficient machining with smaller diameter tools. The smaller the diameter of the tool, the higher the required spindle speed (rpm), and the spindle of most conventional machine tools is difficult to achieve such a high speed. Even if it can be achieved, the machine spindle will continue to operate under the limit state. Big stress. Conventional CNC machining machines that use tools with diameters less than 0.5" (12.7 mm) at 10,000 r/min or less often result in unreasonable feed and costly tool damage.
2. The glass slide is at the bottom, which is the carrier for the material you want to observe, that is, you want to put something on it.
3. The cover glass is smaller than the slide glass. The glass slide is mainly used to hold the observation objects. The cover glass is covered on the slide glass and used for fixing.
4. The glass slide is a thicker piece of glass in the transfer slide, which is used to carry the real object. The cover fragment is the small round or square thin one.
5. Mounting is a general term for a set of things, including slides, coverslips and loaded objects