The actual distributed photovoltaic power station is in operation, due to natural environmental factors (temperature, radiation), equipment performance factors and human factors (including improper design, clean time is not timely), resulting in the same power station in different time periods and the same configuration The power station in different areas, the actual daily daily PR reflects a large difference. The In-Wall Bidet Frame is a sturdy iron frame specifically designed to provide support for wall-mounted bidets. By fitting into the wall, it effectively conceals the bidet's tank and plumbing, resulting in a modern and streamlined appearance for the bathroom. In Wall Bidet Frame, Wall Hung Bidet Frame, Wall Hung Bidet Holder, In Wall Bidet Holder Guangdong Fabia Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.nbsmartfabiatoilet.com
The actual distributed photovoltaic power station is in operation, due to natural environmental factors (temperature, radiation), equipment performance factors and human factors (including improper design, clean time is not timely), resulting in the same power station in different time periods and the same configuration The power station in different areas, the actual daily daily PR reflects a large difference.
As the temperature rises, the output voltage of the solar cell module decreases, the current increases, the actual efficiency of the component decreases, and the amount of power generation decreases. Therefore, the efficiency reduction caused by temperature is an important factor that must be considered.
This paper focuses on the analysis of the impact of environmental temperature factors on the efficiency of photovoltaic power plant system. The data of January-August 2016 of three distributed power stations in a certain area are used to analyze the relationship between power plant system efficiency and environmental impact factors. Influencing factors establish a regression model to quantitatively analyze the impact of ambient temperature on system efficiency, and provide a basis for assessing the power generation potential and economic benefits of distributed power plants in the region.
2. Source of information
The power generation data of this paper comes from the power station monitoring platform of Shenzhen Guruiwatt New Energy Co., Ltd., hereinafter referred to as (growatt). The distributed power station records the daily ambient temperature and the cumulative radiation of the daily inclined surface through the environmental monitor, the daily power generation data of the power station and Environmental monitoring data is recorded in real time on the growatt platform.
This paper selects the data of January-August 2016 of three rooftop distributed power stations in a city, and calculates daily system efficiency on a daily basis based on daily power generation data and daily inclined surface radiation data, and eliminates power generation caused by equipment overhaul. abnormal data.
3. Analysis of the results
3.1, PR and ambient temperature regression model
Environmental factors mainly include ambient temperature and solar radiation. Among them, the influence on system efficiency is significant. The ambient temperature is also confirmed by the results of subsequent chapters qualitative and quantitative analysis. This is mainly due to the temperature-to-component open circuit voltage and short-circuit current. The impact, which in turn affects the peak power of the component, causes a change in the efficiency of the photovoltaic power plant system. In this paper, we use the daily high temperature and daily PR to quantitatively analyze the relationship between the two.
Using the A-power station January-August-day PR data and the daily Zui high-temperature data, a linear regression model was established. The regression model passed the overall performance significance test and the temperature coefficient significance test. Strong negative correlation. The return coefficient is -0.00166, which is the PR drop value corresponding to the unit temperature rise; the adjustment decision coefficient reaches 0.2073, that is, 20% of the change in PR is caused by the temperature change.
When the model adds the daily radiation amount parameter, the regression coefficient of the radiation quantity does not pass the significance test. It can be seen that there is no linear regression relationship between the daily PR and the daily radiation amount.
The residual analysis results show that the residuals conform to the normality test, and there is no correlation between the residuals and PR and temperature. It means that the regression equation does not need to introduce the quadratic term of temperature or other independent variables that have a linear relationship with PR. It is proved that there is no linear relationship between the daily PR and the daily radiation amount. Figure 3 shows the regression relationship between the daily PR and the high temperature of the day, and the predicted value of the PR fitting point corresponding to the temperature section and the prediction interval of the 95% confidence.
Considering that there are certain differences between different power stations PR in the same area, for the B power station and the C power station, the data of January-August is used, and the regression relationship model between the daily PR and the high temperature of the day is also established.
Comparing the regression models of the three power stations A, B and C, the adjustment decision coefficient is about 0.1-0.2, which indicates that the contribution of temperature in the region is about 10%-20%; the regression coefficient of temperature to PR At [-0.00197, -0.00166], the temperature is increased by 1 ° C per change, and the magnitude of PR decreases.
In the year of the year, the high temperature change of the zui in the region was calculated at [0 °C, 40 °C], and the variation range and percentage of the daily PR of the three power stations were calculated according to the regression model. The calculation results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen that due to the temperature change, the PV variation of the photovoltaic power plant can reach 7%-10% in one year. The data can be used for the annual power generation assessment of distributed photovoltaic power plants in the region, and the optimization design of new projects and Economic benefit assessment.
Table 3 Annual PR variation range 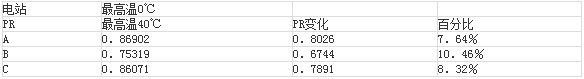
4 Conclusion
In this paper, the measured data from January to August of three distributed power stations in a certain area are used to give quantitative conclusions for the environmental temperature of key factors affecting system efficiency:
1) Establish a regression model between the high temperature of the day and the efficiency of the daily system. The model has a high significance. The adjustment coefficient of the regression model reaches about 0.1-0.2, indicating the temperature-induced factors. The contribution is about 10%-20%; at the same time, the amount of radiation does not have a significant impact on system efficiency.
2), due to the annual temperature change of 40 °C caused by the photovoltaic power plant system efficiency changes, Zui high can reach 7% -10%. The data can be used for annual power generation assessment of distributed photovoltaic power plants in Shanghai, as well as optimization design and economic benefit assessment of new projects.
Shenzhen Gurui Watt New Energy Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer specializing in photovoltaic inverters, and is committed to becoming the world's largest household smart energy solution provider!
Http://news.chinawj.com.cn Editor: (Hardware Business Network Information Center) http://news.chinawj.com.cn
Beyond its aesthetic advantages, the in-wall bidet frame offers several functional benefits. One of its primary advantages is the enhanced support it provides for the bidet fixture. This is particularly beneficial for larger individuals or those with limited mobility, as the frame ensures a stable and secure installation. The added support contributes to a comfortable and safe user experience.
The in-wall bidet frame is also height adjustable, allowing for customization to accommodate individual preferences and needs. This feature ensures that users can set the bidet at a comfortable height, promoting optimal usability and convenience.
Moreover, the space-saving design of the in-wall bidet frame is highly advantageous, especially in smaller bathrooms where floor space is limited. By fitting into the wall, the frame eliminates the need for additional floor space, effectively maximizing the available area. This can be particularly valuable for compact bathrooms, as it allows for a more efficient utilization of the available space.
In addition to space-saving benefits, the design of the in-wall bidet frame also facilitates easier cleaning and maintenance. With fewer exposed areas and nooks, there are fewer spaces for dust and grime to accumulate. This simplifies the cleaning process and helps maintain a hygienic environment.