Kitchen Sink Faucets,Touch Kitchen Faucet,Retractable Kitchen Faucet,Black Steel Hose Faucet Yuyao Zelin Sanitary Ware Co., Ltd , https://www.kitchen-sinkfaucet.com
Chemical production is characterized by inflammable, explosive, toxic and harmful, and corrosive, and the risk is greater than other industries. Therefore, in the chemical production, we actively promote modern safety management, apply the methods and principles of system engineering to identify the conditions and possible consequences of various events that affect the normal operation of the system, and pre-establish countermeasures to eliminate and control these events. It can achieve the purpose of preventing accidents and achieving system safety.
Pre-hazard analysis method
Pre-hazard analysis method (PHA, Preliminary Hazard Analysis) refers to the assumption that various risk factors may exist in the system before an engineering activity (including design, construction, production and maintenance). The method of questioning is listed, and then a macroscopic and summary analysis of the possible consequences is made, and safety precautions are proposed.
Before conducting the pre-hazard analysis, a team of engineers, operators and managers should be formed according to the actual situation of the project . Based on the study of PID, operating procedures, process descriptions and other related information, Analyze the work according to the following procedure.
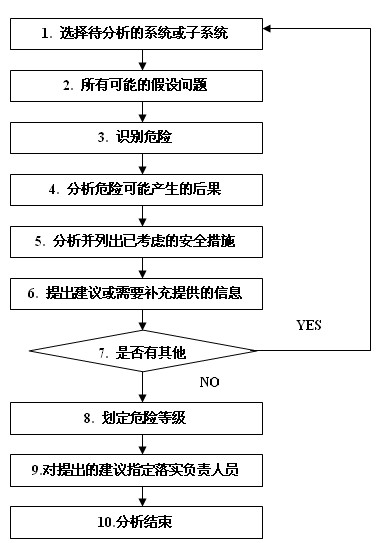
Assumption analysis process description
Step 1: Select the system or subsystem to be analyzed
The object of research and analysis should be an indivisible subsystem, such as: the subsystem of the raw material tank area is the storage tank and the pump.
Step 2: Raise all possible hypothetical questions
The hypothetical problem is used to identify the various potential risk factors present in the system. For example, if a hazardous material overflows to the ground, the operator may be poisoned or corroded by smoke or steam.
To ensure the comprehensiveness of the problem, the analysis team can pre-collect information on similar projects and prepare a standard checklist. It is assumed that the problem can be proposed and organized according to the following list according to the standard list: related to safety measures failure → related to equipment (hardware or system) failure → related to human error → related to external events, and so on.
Team members should verify the assumptions presented by the analysis on a case-by-case basis and decide whether the hypothesis of double risk should be considered and documented. The double-hazard condition is that two events occur simultaneously before the danger is detected (eg, hardware failures and human error). The team should judge the credibility of the double event. For example, it is possible that the pump and the pump outlet check valve fail at the same time. Assumptions that cannot occur at the same time are not recorded.
Step 3: Identify the danger
Combined with the hypothetical questions presented in Step 2, analyze and document the potential hazards associated with the chemical properties (toxicity, flammability, reactivity, etc.) and process operating conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.) present in each hypothesis .
Step 4: Analyze the possible consequences of the danger
Analyze and identify the possible consequences of each hazard, and some hazards can have multiple consequences. The analysis team should document the discussion of the hazards identified in all of the three steps. Even if some risks have no substantial consequences, they are recorded, so that the analysis of the dangers of the members can be seen.
Step 5: Analyze and list the security measures that have been considered
Analyze and document security measures that are already in place or designed in the system. These safety measures are used to prevent, monitor, and reduce the consequences of the risks posed by the proposed assumptions.
It is very important to document the existing or already designed security measures in the system, as it can be seen from which methods and means have been taken, and also to help the team members to consider whether further supplements or modifications should be made. For hypothetical questions that pose a high level of risk, the team leader should ensure that sufficient safety measures are listed.
Step 6: Make a suggestion or need to supplement the information provided
In the “Recommendations†column of the analysis form, the group agrees on the rectification of existing security measures, lists the documents or information that need to be supplemented, or whether further research analysis is needed. The “recommendations†should closely follow the consequences listed in step four.
Step 7: Is there another system?
Repeat steps 1 through 6 for other systems or subsystems .
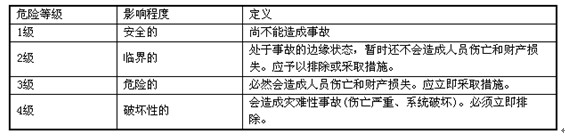
Step 8: Delineate the hazard level
All risk factors are assigned based on the established risk level classification definition. Because the same consequences may occur in different systems, this work is best done after the analysis of all systems is completed, which ensures the consistency of the hierarchy, and also simplifies the work and improves work efficiency.
The classification of hazard levels can be found in the following table:
Step 9: Designate responsible personnel for the proposed recommendations
The proposed “recommendations†should be assigned to the appropriate personnel or groups to ensure that the recommendations are implemented in subsequent work.
After the above steps are completed, the person in charge of the analysis team shall be responsible for collating the complete analytical worksheet and completing the analytical research report on this basis.
Pre-hazard analysis example
The following table is part of the pre-hazard analysis of the liquid ammonia tank area. for reference only.
Pre-hazard analysis worksheet
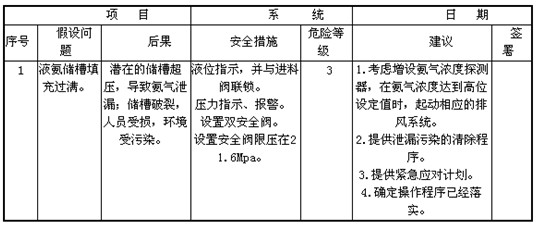
Apply pre-hazard analysis methods to identify hazardous materials, unsafe process routes and equipment, identify and analyze potential hazards in people, objects, and environments that may affect the system prior to each activity in the chemical project implementation. And on this basis, put forward security measures. This method is easy to operate and easy to grasp. The safety measures analyzed have the characteristics of comprehensive consideration and strong pertinence. It can be widely used in various stages of engineering construction and project implementation. It is an effective means to reduce and prevent accidents and achieve system safety. .