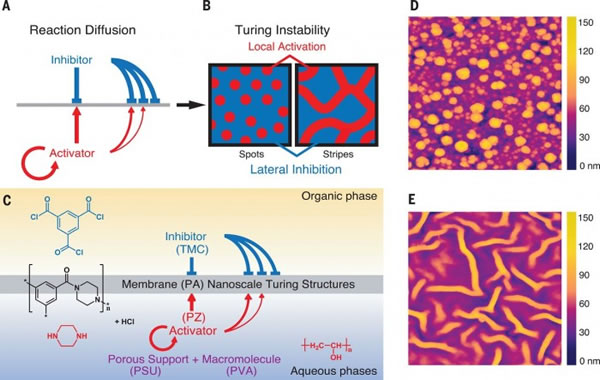
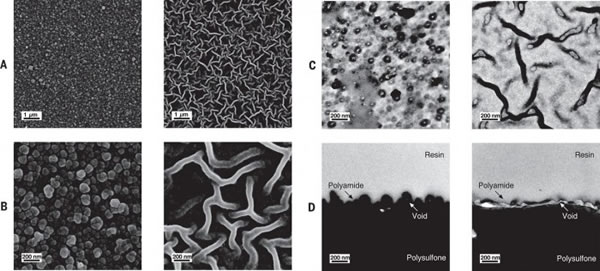
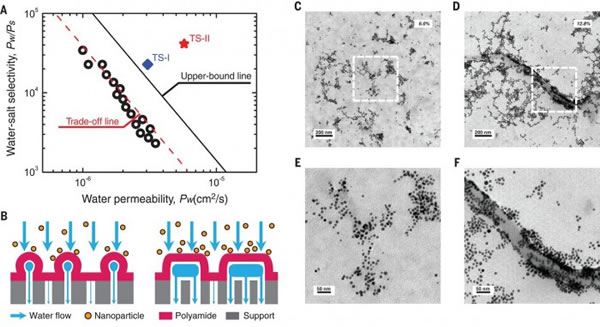
The Chinese research team developed a new type of nanofiltration membrane using the “Turing Structureâ€. Its water permeability rate is three to four times that of traditional nanofiltration membranes, and it is expected to improve the advanced treatment of drinking water, brackish water desalination, and industrial water recycling. Water efficiency and reduce costs. The research published on the 3rd in the United States "Science" magazine showed that Professor Zhang Lin of the School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering of Zhejiang University proposed the "reaction-diffusion equation" and film proposed by the father of computer and artificial intelligence and British scientist Alan Turing. The combination of the studies produced the first-ever nanoscale "Turing" on the film. Turing published the article "The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis" in 1952, trying to explain the chemical mechanism behind complex life forms with a simple mathematical formula. He believes that any repetitive natural patterns are generated by the interaction of two things with specific characteristics (such as molecules, cells, etc.). According to his "reaction-diffusion equation," these two components are caused by differences in diffusion. The system is unstable and eventually forms "Turing Structures" such as stripes, stripes, and spots. Turing speculates that the pattern on the surface of organisms such as zebra may be the result of this reaction-diffusion system. Nanofiltration membranes are functional semipermeable membranes with a pore size of 1 nanometer or more that allow certain molecules or ions to pass through. They can remove specific organic substances, pigments, and salts from water, and are mainly prepared by "interfacial polymerization." The researchers first dissolved the two small molecules of piperazine and trimesoyl Chloride in water and oil, and the two small molecules polymerized at the interface of water and oil, forming a flat and dense layer with a thickness of about 100 nanometers within seconds. The polymer film. However, the difference in diffusion rates of piperazine and trimesoyl chloride is not sufficient to produce a "Turing structure." Subsequently, Zhang Lin's team added polyvinyl alcohol to the polymerization reaction, which reduced the diffusion rate of piperazine and eventually produced a nanofiltration membrane with a nano-scale "Turing structure". By adjusting the concentration of polyvinyl alcohol, different "Turing structures" such as bubbles and tubes can also be obtained. Prof. Zhang Lin told Xinhua News Agency reporters that the hollow tubular or bubble “Turing structure†can provide a larger effective water transfer area, so the material has higher water flux and salt retention performance. "This technology only adds the process of adding hydrophilic macromolecules in the traditional process of preparing nanofiltration membranes. This method does not adjust the traditional process, so it is easy to achieve industrialization." Zhang Lin said. Sodium phosphates have many applications in food and for water treatment. For example, sodium phosphates are often used as emulsifiers (such as in processed cheese), thickening agents, and leavening agents for baked goods. They are also used to control pH of processed foods. They are also used in medicine for constipation and to prepare the bowel for medical procedures. Moreover, they are used in detergents for softening water, and as an efficient anti rust solution. Tetrasodium Pyrophosphate,Disodium Dihydrogen Pyrophosphate,Trisodium Phosphate Tsp,Sodium Phosphate Jiangsu Kolod Food Ingredients Co., Ltd. , https://www.kolodchem.com