Recently, Professor Zeng Jie's group at the Hefei National Research Center for Microscale Material Science and the School of Chemistry and Materials Science of the University of Science and Technology of China used tin nickel disulfide nanosheets doped with different nickel contents as catalysts to achieve efficient electroreduction of carbon dioxide to formic acid and carbon monoxide. This nickel-doped tin disulfide nanosheet catalyst exhibits high activity and high stability in the carbon dioxide electroreduction reaction. The result, titled Nickel Doping in Atomically Thin Tin Disulfide Nanosheets Enables Highly Efficient CO2 Reduction, was published on August 15 in the German Journal of Applied Chemistry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10954-10958), The co-first authors of the thesis are master student Zhang An, doctoral student He Rong and master student Li Huiping. In the electroreduction of carbon dioxide, the activation of CO2 molecules has always been a research difficulty in the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2. In the standard case, the standard electrode potential required for the activation of CO2 molecules into CO2-anions in aqueous solution is -1.9 V vs RHE relative to standard hydrogen. Generally, the activation of CO2 molecules involves the transfer of electrons from the catalyst to the CO2 molecules, and this process is closely related to the electronic structure of the catalyst. Therefore, the efficient activation of CO2 molecules can be achieved by adjusting the electronic structure of the catalyst. Based on this concept, the researchers obtained SnS2 nanosheet catalysts with different nickel doping by adjusting the content of nickel introduced based on two layers of SnS2 nanosheets with atomic thickness. The SnS2 nanosheet catalyst with appropriate nickel content achieves efficient activation of CO2 molecules, thereby enhancing the performance of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction reaction. In the CO2 electrocatalytic reduction reaction, at a voltage of -0.9 V vs RHE, the Faraday efficiency of CO2 reduction to effective carbon products is as high as 93% and the current density reaches -19.6 mA / cm2. The mechanism study further shows that nickel doping will produce defect states near the conduction band of SnS2, and its work function will also be reduced. This effect helps to achieve efficient activation of CO2 and improve the performance of CO2 electroreduction reaction. This work not only prepared efficient nickel-doped SnS2 nanosheets as carbon dioxide electroreduction catalysts, but also provided a method for rational design of electrocatalysts. This research was supported by the National Academy of Sciences Key Frontier Science Research Project, the National Major Scientific Research Program, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. SUN YAT INDUSTRY LIMITED , https://www.ernte-eu.com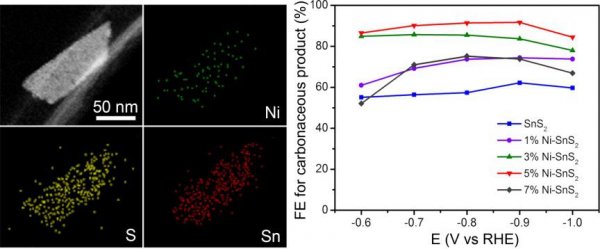
Nickel-doped tin disulfide nanosheets and the performance of electroreduction of carbon dioxide